Animate a 2D tour path with a scatterplot.
display_xy(
center = TRUE,
axes = "center",
half_range = NULL,
col = "black",
pch = 20,
cex = 1,
edges = NULL,
edges.col = "black",
edges.width = 1,
obs_labels = NULL,
ellipse = NULL,
ellc = NULL,
ellmu = NULL,
ellmarks = TRUE,
palette = "Zissou 1",
shapeset = c(15:17, 23:25),
axislablong = FALSE,
...
)
animate_xy(data, tour_path = grand_tour(), ...)Arguments
- center
if TRUE, centers projected data to (0,0). This pins the center of data cloud and make it easier to focus on the changing shape rather than position.
- axes
position of the axes: center, bottomleft or off
- half_range
half range to use when calculating limits of projected. If not set, defaults to maximum distance from origin to each row of data.
- col
color to use for points, can be a vector or hexcolors or a factor. Defaults to "black".
- pch
shape of the point to be plotted, can be a factor or integer. Defaults to 20.
- cex
size of the point to be plotted. Defaults to 1.
- edges
A two column integer matrix giving indices of ends of lines.
- edges.col
colour of edges to be plotted, Defaults to "black"
- edges.width
line width for edges, default 1
- obs_labels
vector of text labels to display
- ellipse
pxp variance-covariance matrix defining ellipse, default NULL. Useful for comparing data with some null hypothesis
- ellc
This can be considered the equivalent of a critical value, used to scale the ellipse larger or smaller to capture more or fewer anomalies. Default 3.
- ellmu
This is the centre of the ellipse corresponding to the mean of the normal population. Default vector of 0's
- ellmarks
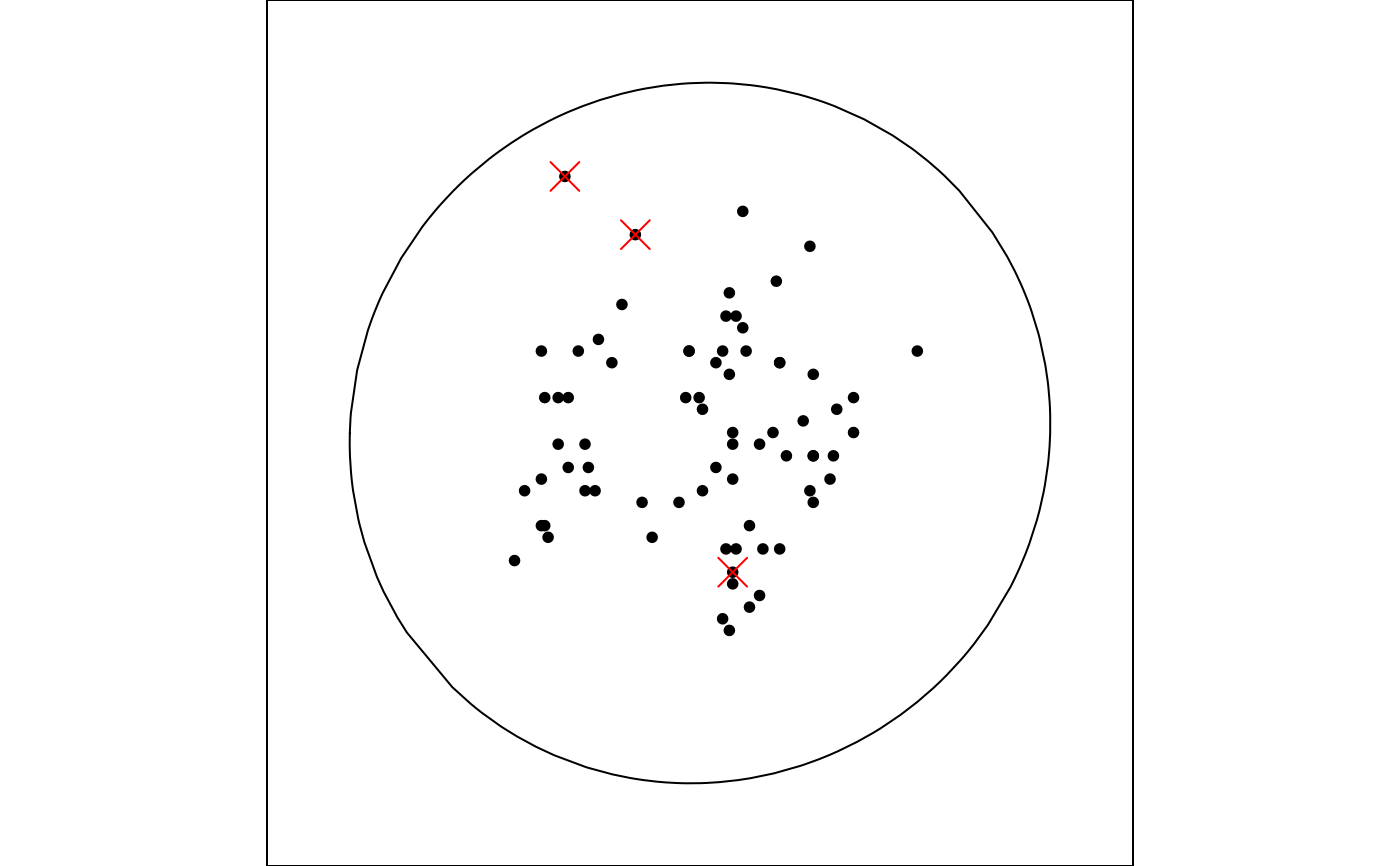
mark the extreme points with red crosses, default TRUE
- palette
name of color palette for point colour, used by
hcl.colors, default "Zissou 1"- shapeset
numbers corresponding to shapes in base R points, to use for mapping categorical variable to shapes, default=c(15:17, 23:25)
- axislablong
text labels only for the long axes in a projection, default FALSE
- ...
other arguments passed on to
animateanddisplay_xy- data
matrix, or data frame containing numeric columns
- tour_path
tour path generator, defaults to 2d grand tour
Examples
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
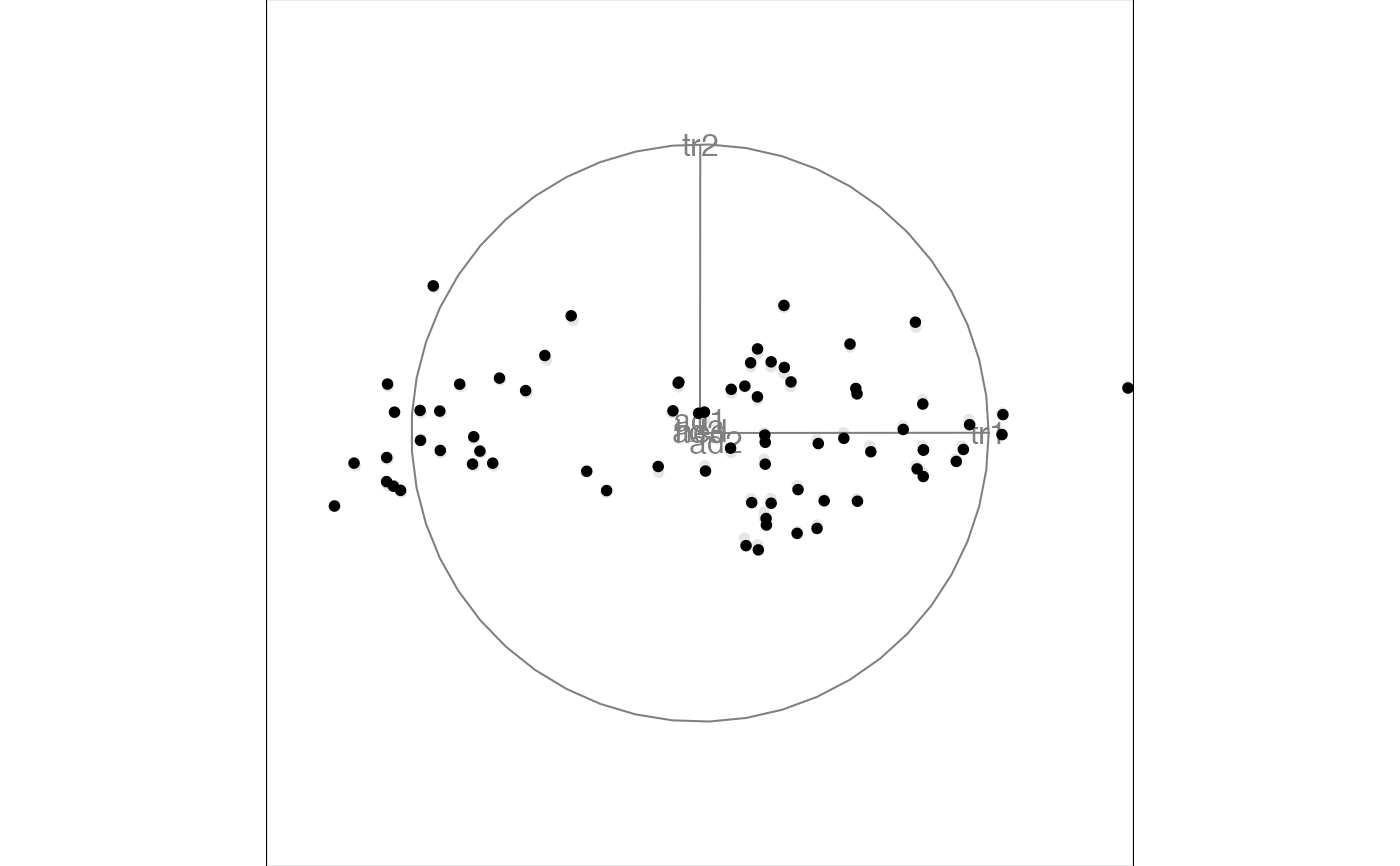
 animate(flea[, 1:6], tour_path = grand_tour(), display = display_xy())
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
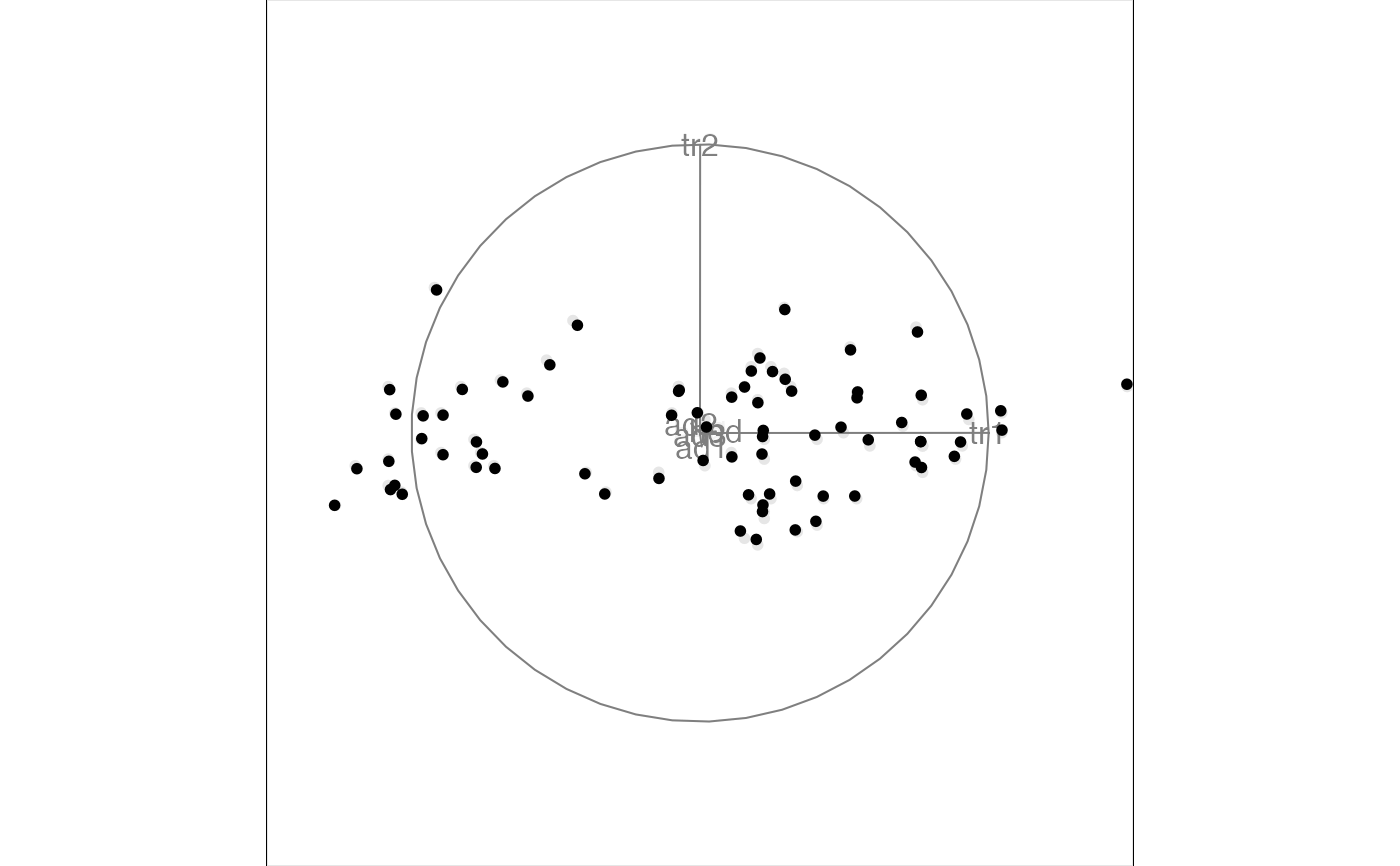
animate(flea[, 1:6], tour_path = grand_tour(), display = display_xy())
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
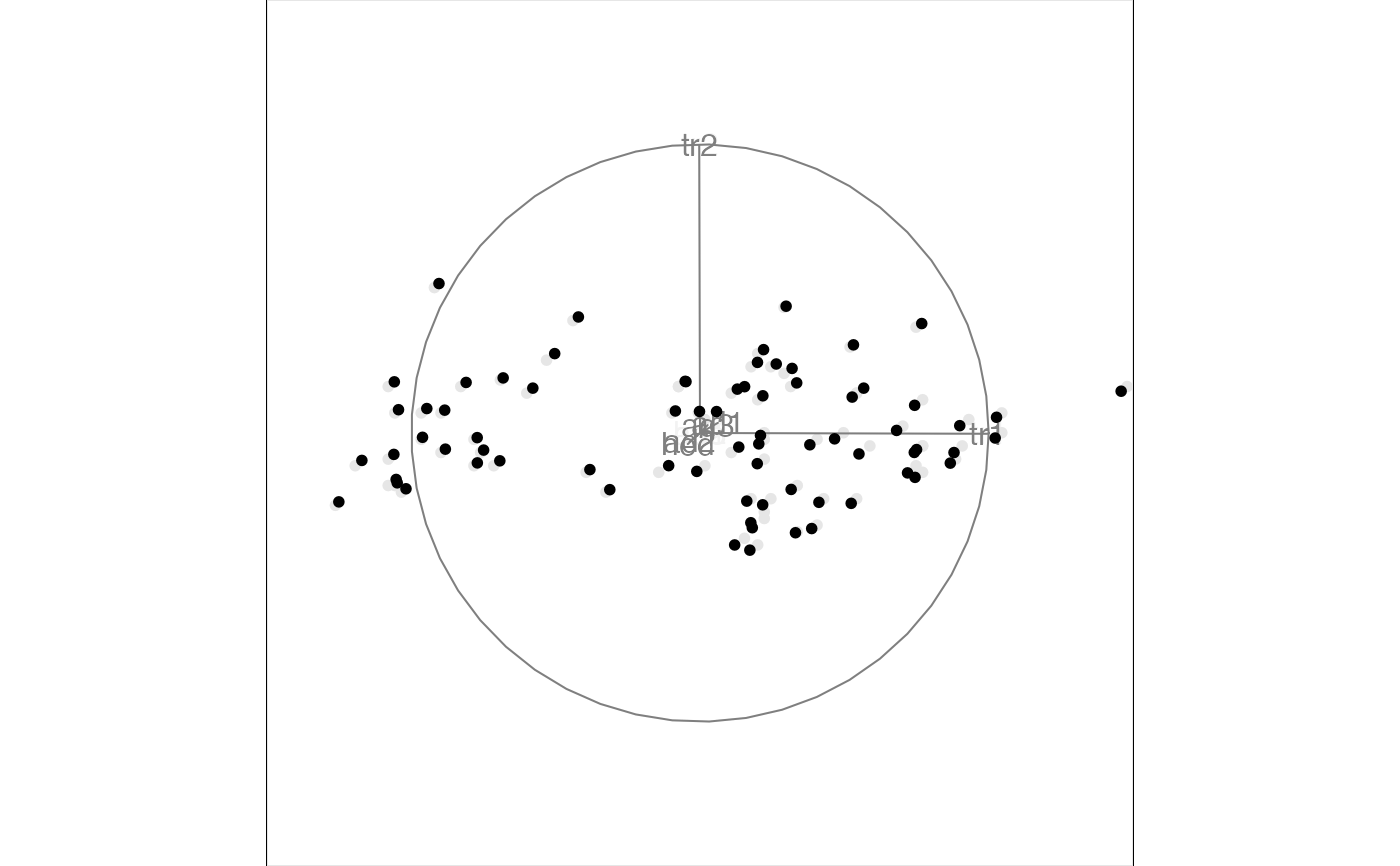
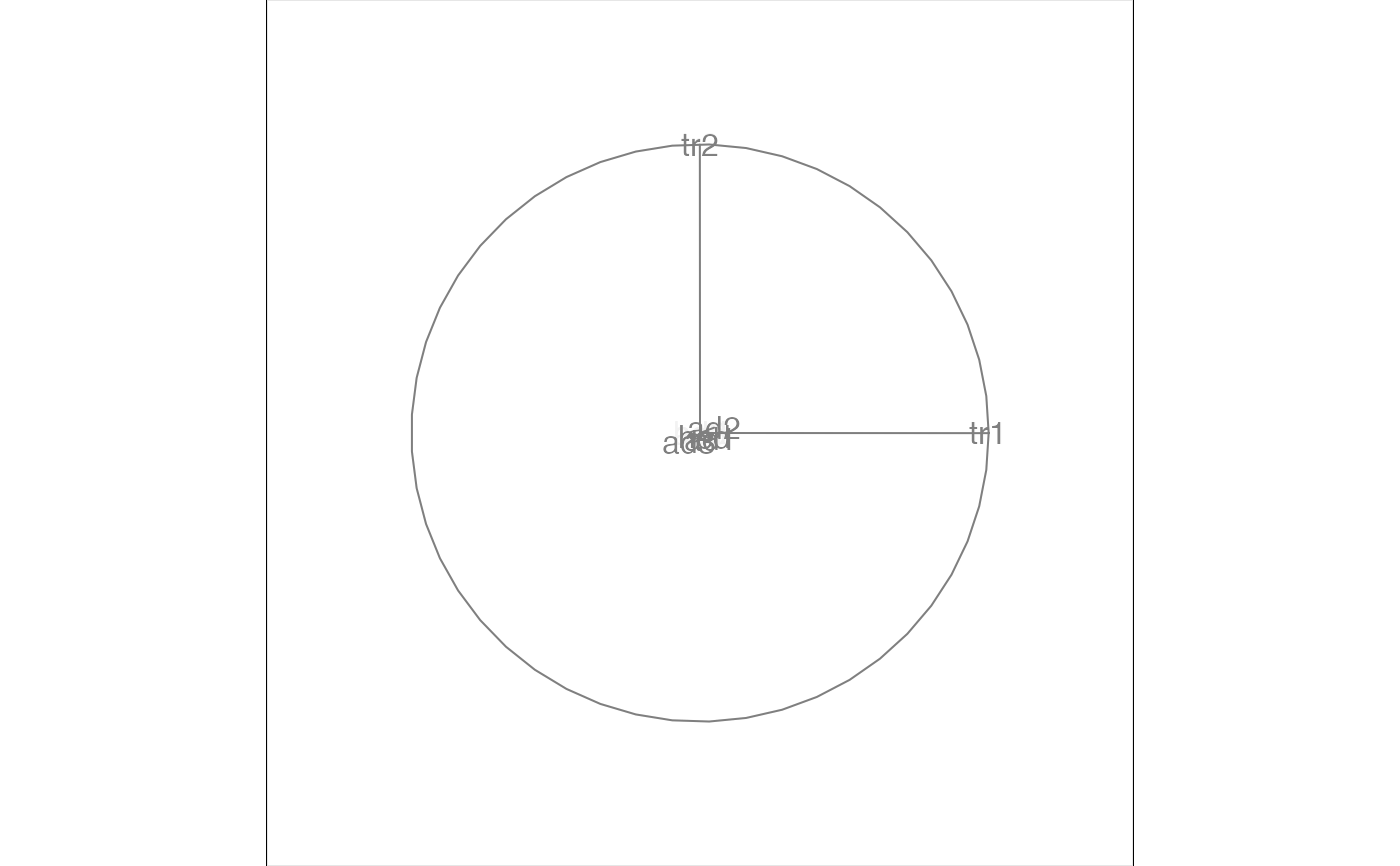 # This won't do anything because the flea data is standardised
# but use rescale option to force scaling before displaying
animate(flea[, 1:6],
tour_path = grand_tour(),
display = display_xy(),
rescale = TRUE
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 0.98
# This won't do anything because the flea data is standardised
# but use rescale option to force scaling before displaying
animate(flea[, 1:6],
tour_path = grand_tour(),
display = display_xy(),
rescale = TRUE
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 0.98
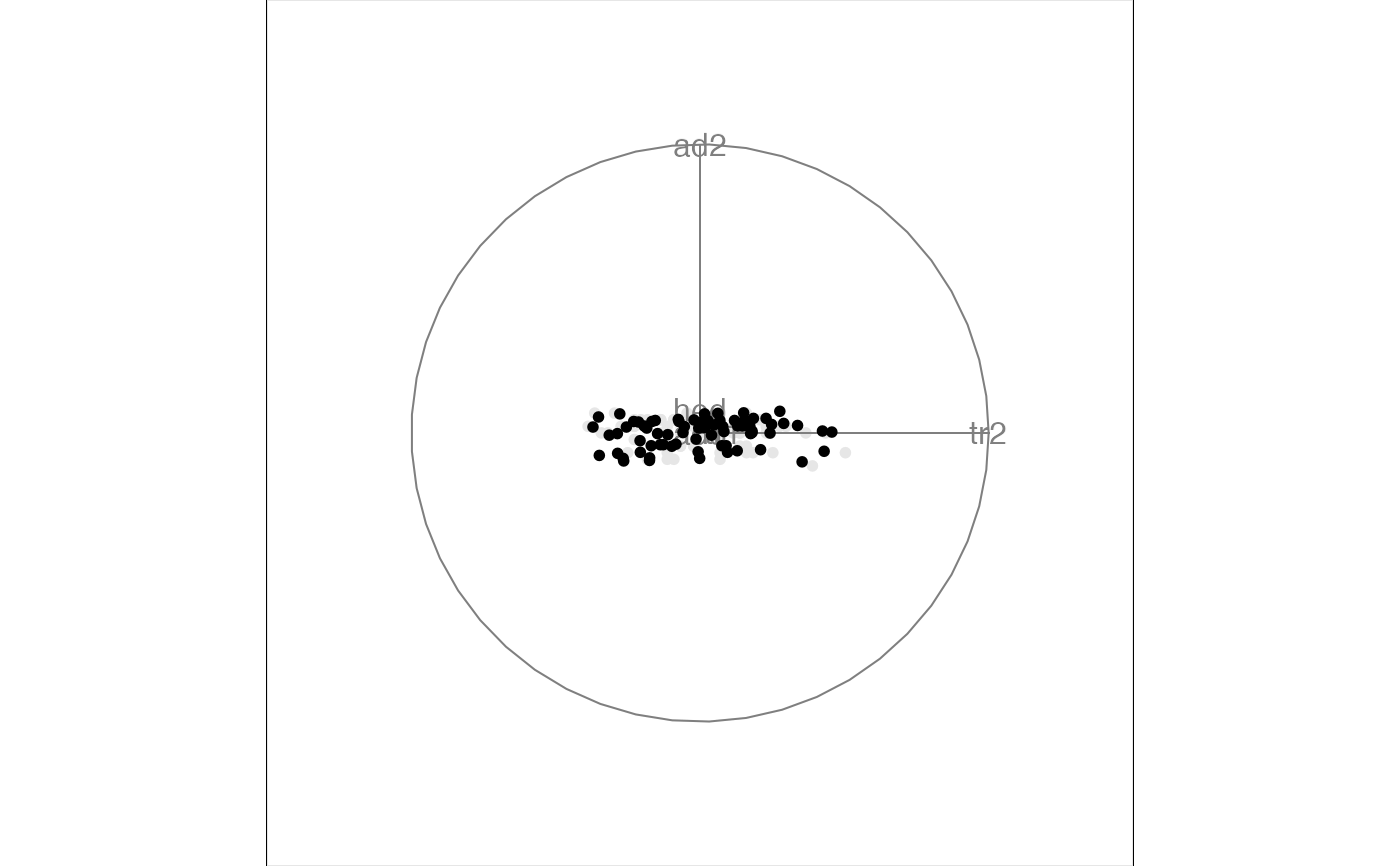
 animate(flea[, 1:6],
tour_path = grand_tour(),
display = display_xy(half_range = 0.5)
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
animate(flea[, 1:6],
tour_path = grand_tour(),
display = display_xy(half_range = 0.5)
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
 animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], tour_path = little_tour())
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], tour_path = little_tour())
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
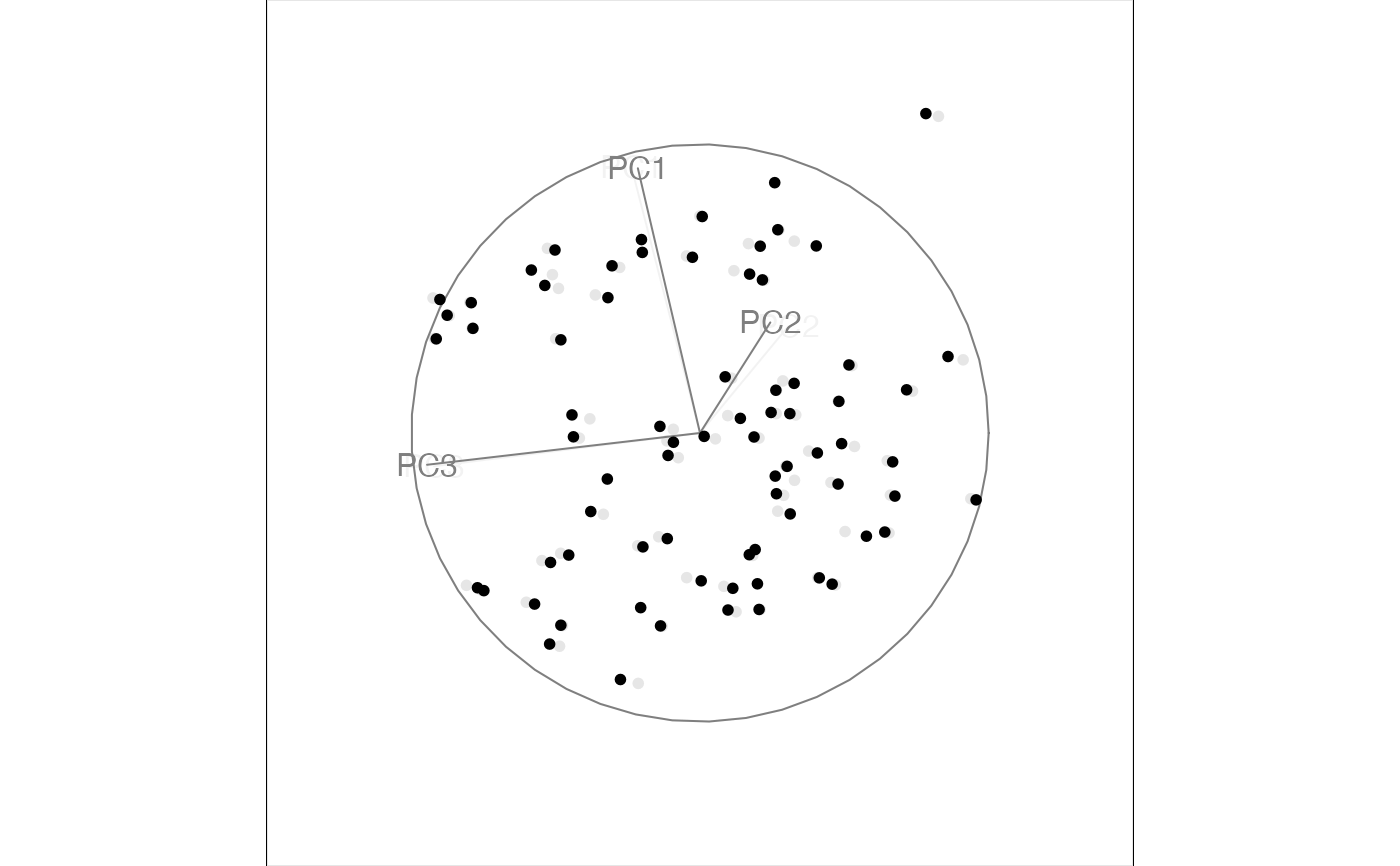
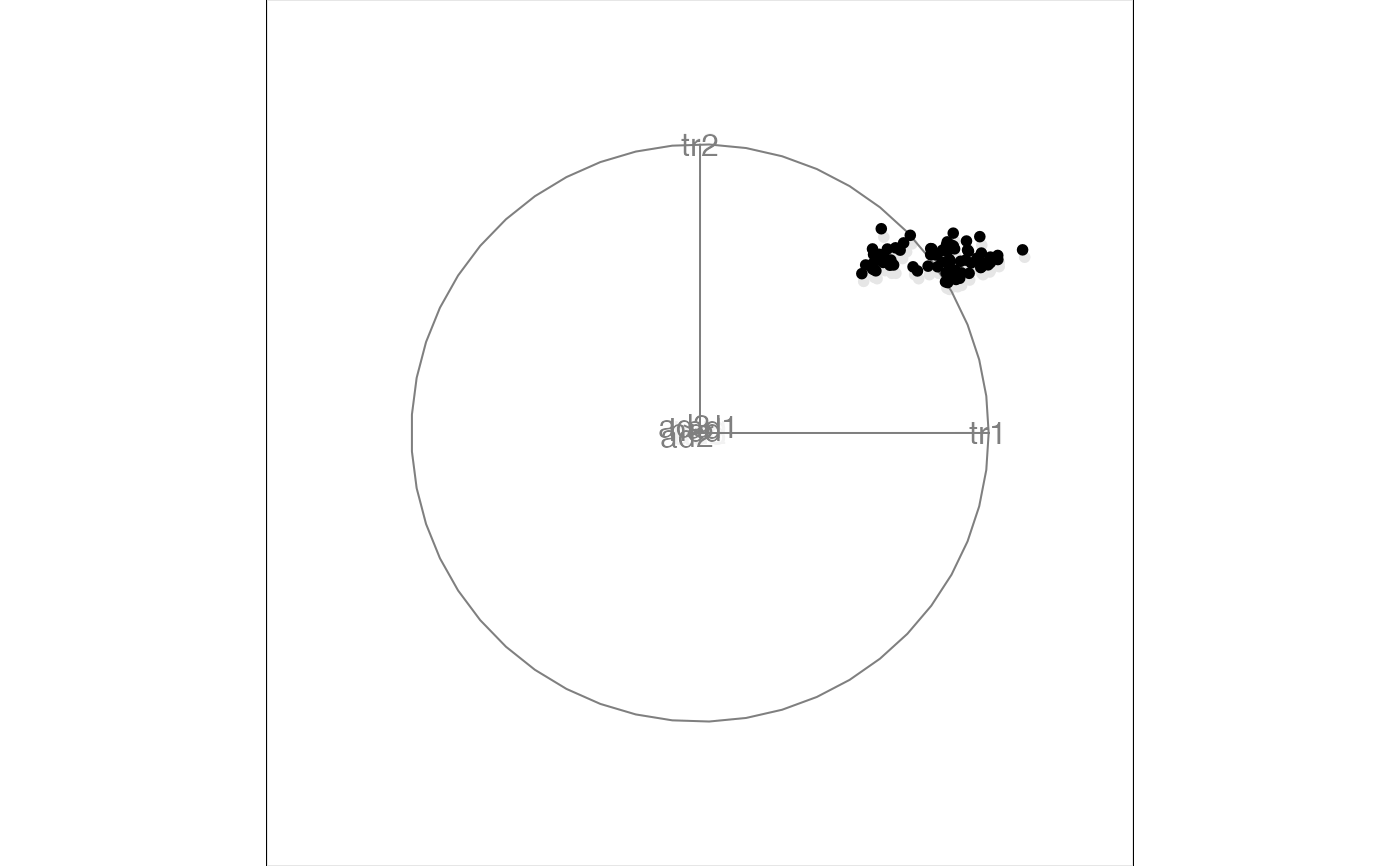
 animate_xy(flea[, 1:3], tour_path = guided_tour(holes()), sphere = TRUE)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Target: 0.857, 1.7% better
#> Using half_range 3.2
animate_xy(flea[, 1:3], tour_path = guided_tour(holes()), sphere = TRUE)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Target: 0.857, 1.7% better
#> Using half_range 3.2
 animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], center = FALSE)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], center = FALSE)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
 # The default axes are centered, like a biplot, but there are other options
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "bottomleft")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
# The default axes are centered, like a biplot, but there are other options
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "bottomleft")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4

 animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "off")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "off")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
 animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], dependence_tour(c(1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2)),
axes = "bottomleft"
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], dependence_tour(c(1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2)),
axes = "bottomleft"
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
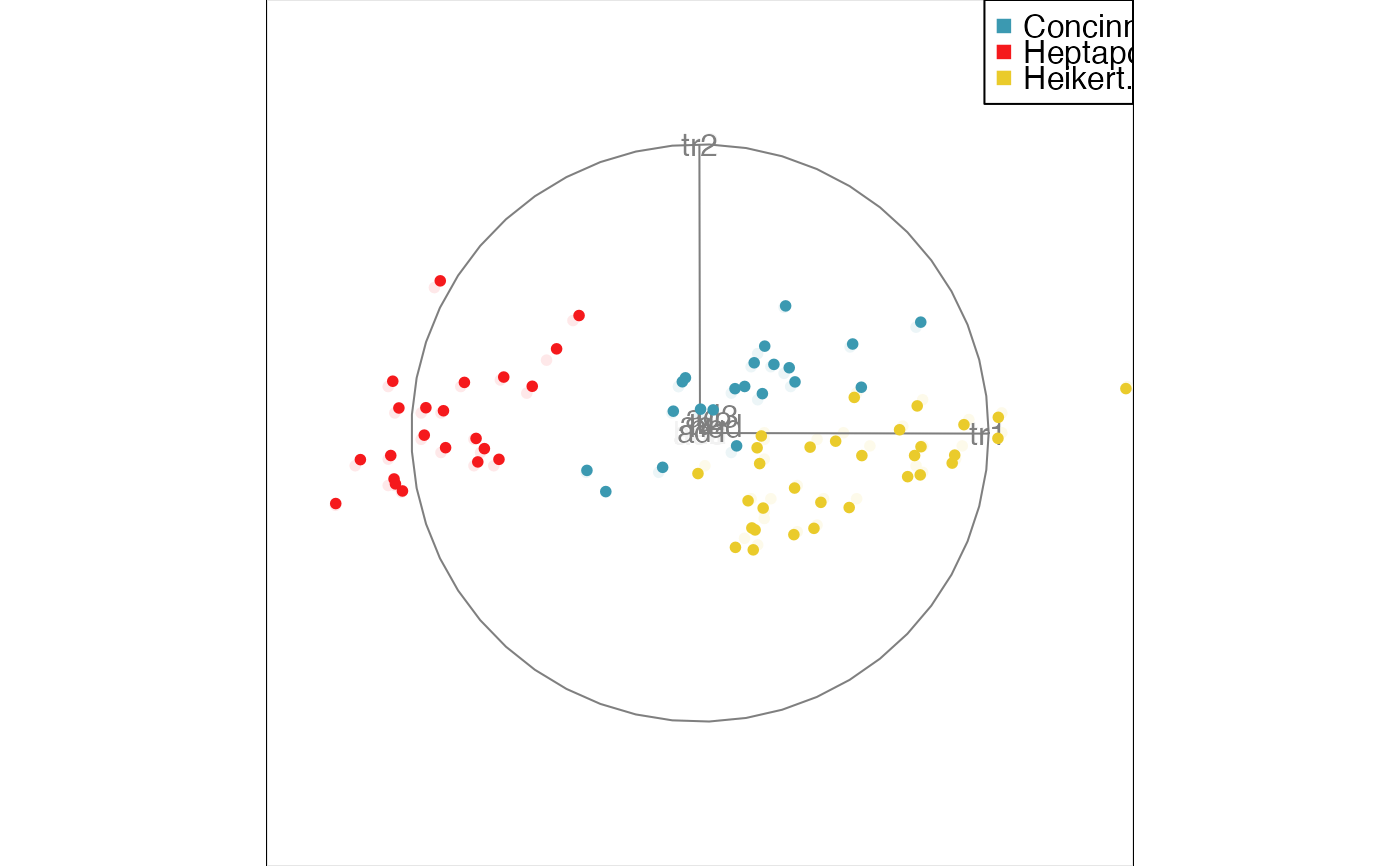
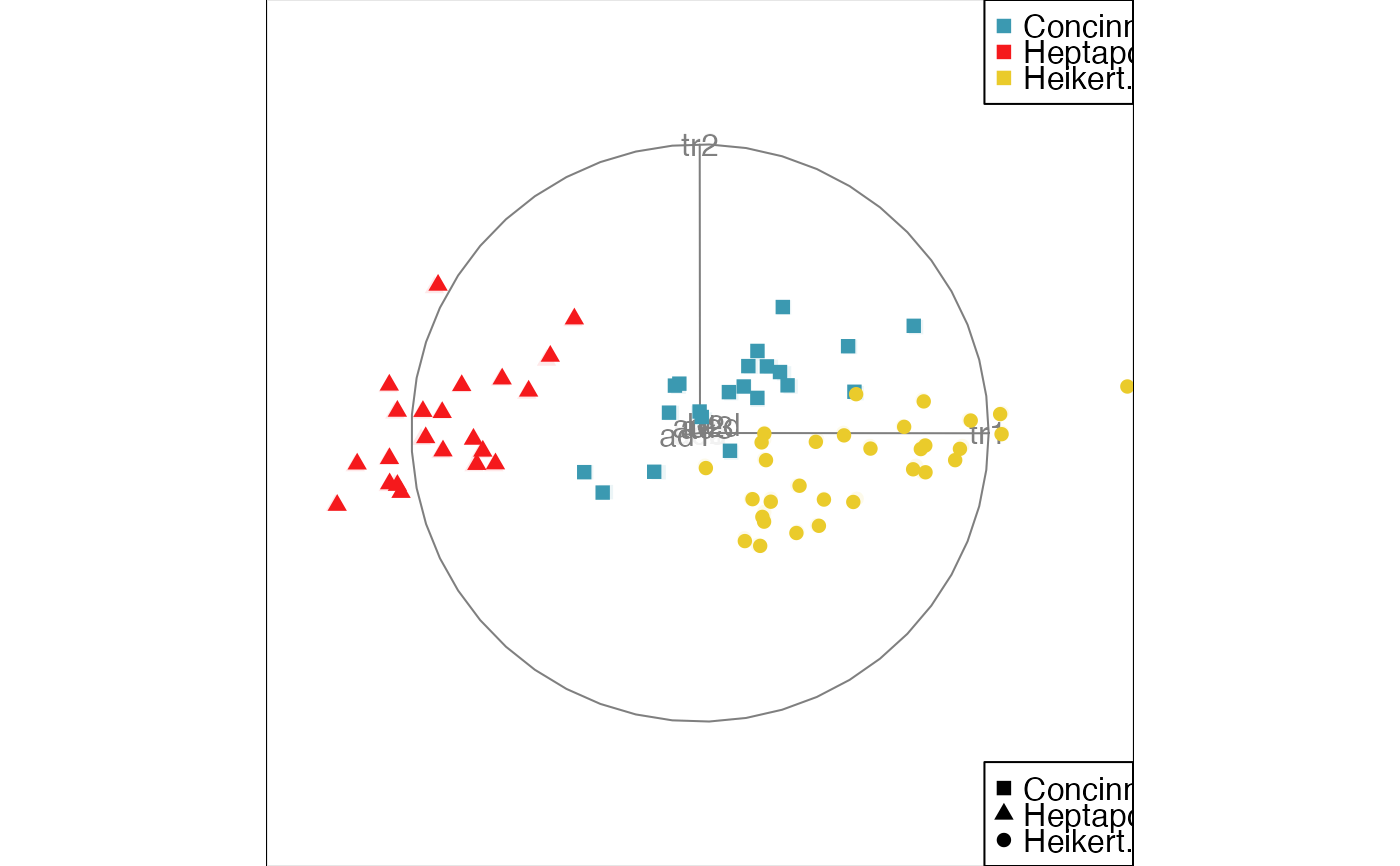
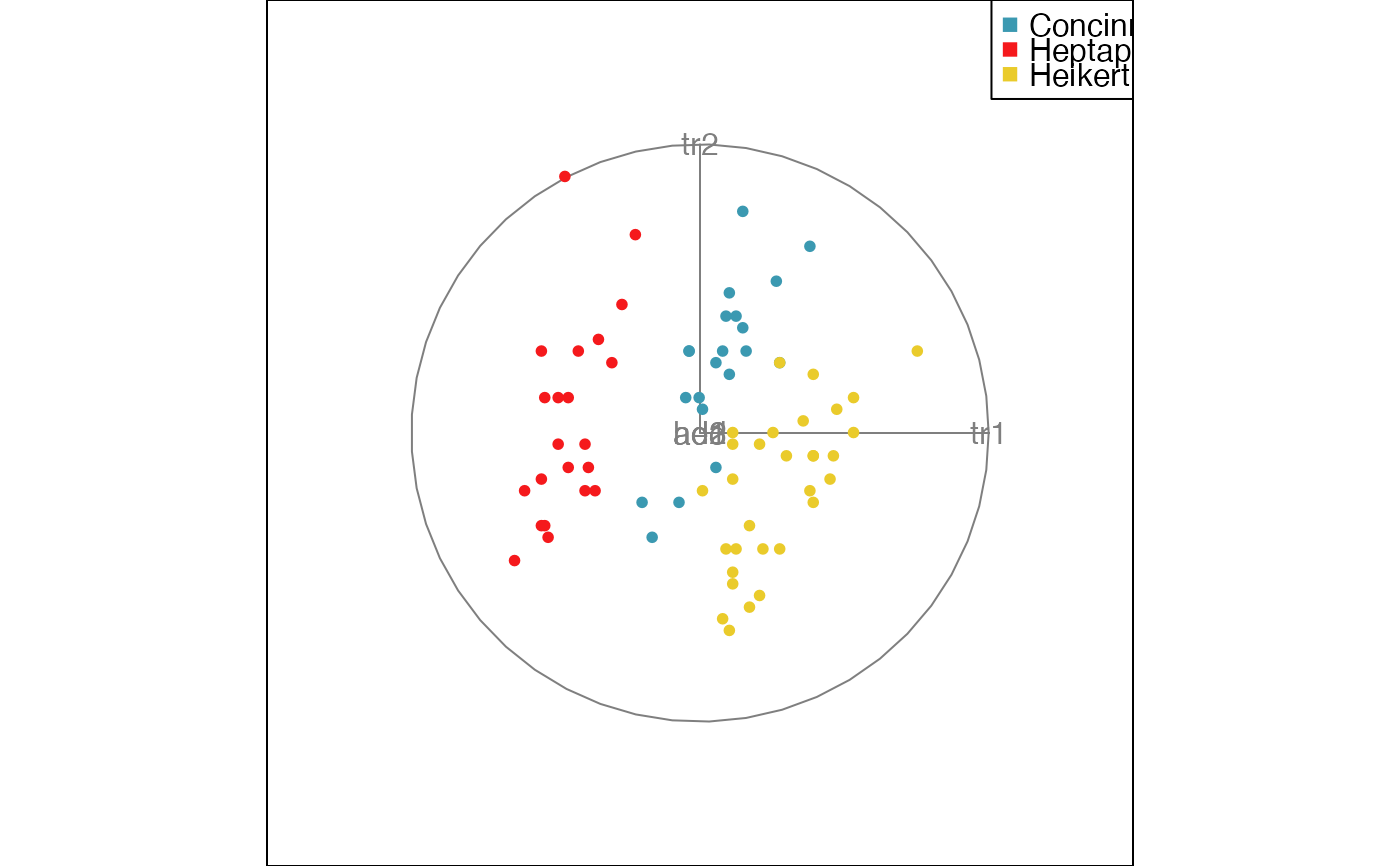
 animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
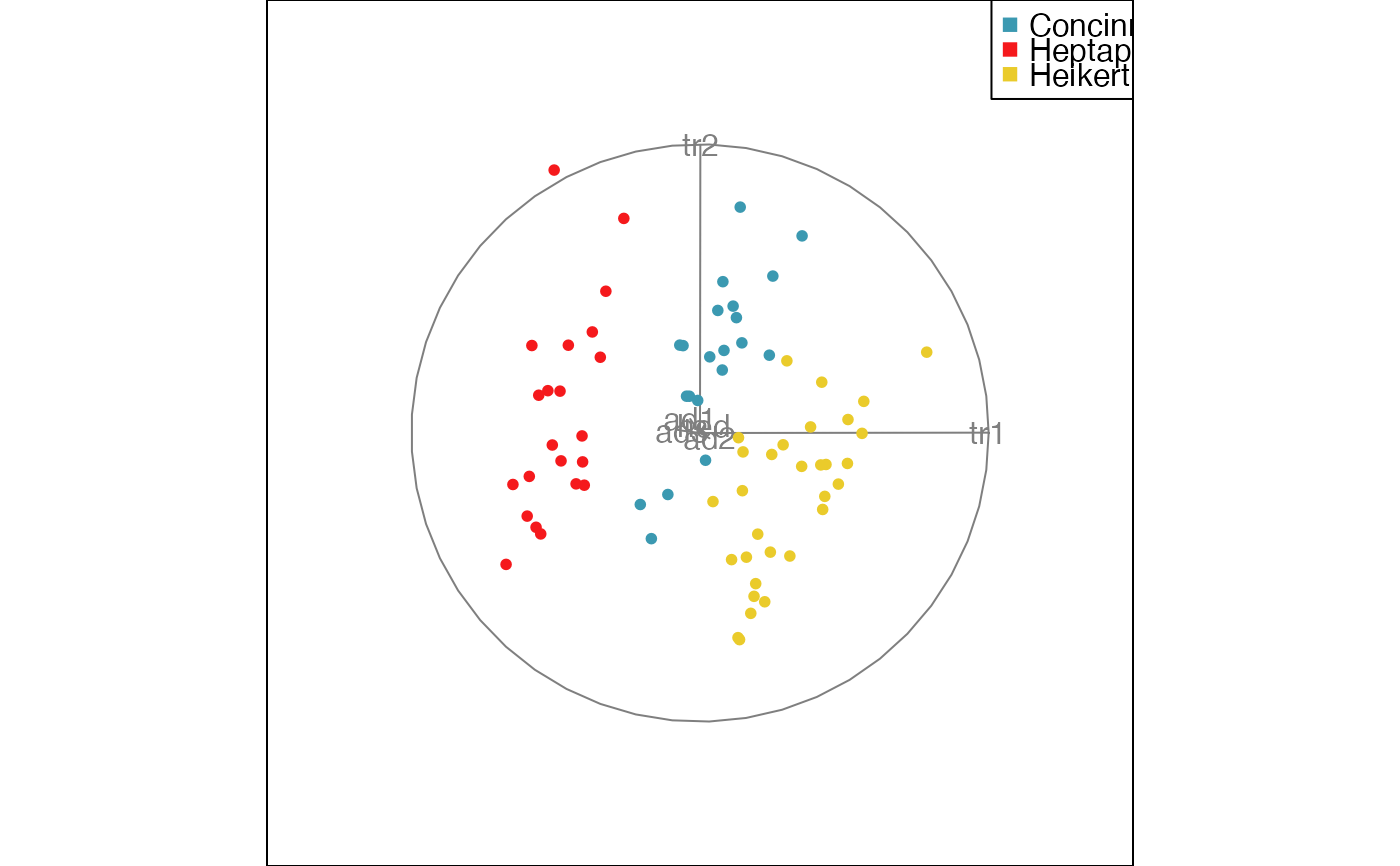 animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species,
pch = flea$species)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species,
pch = flea$species)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
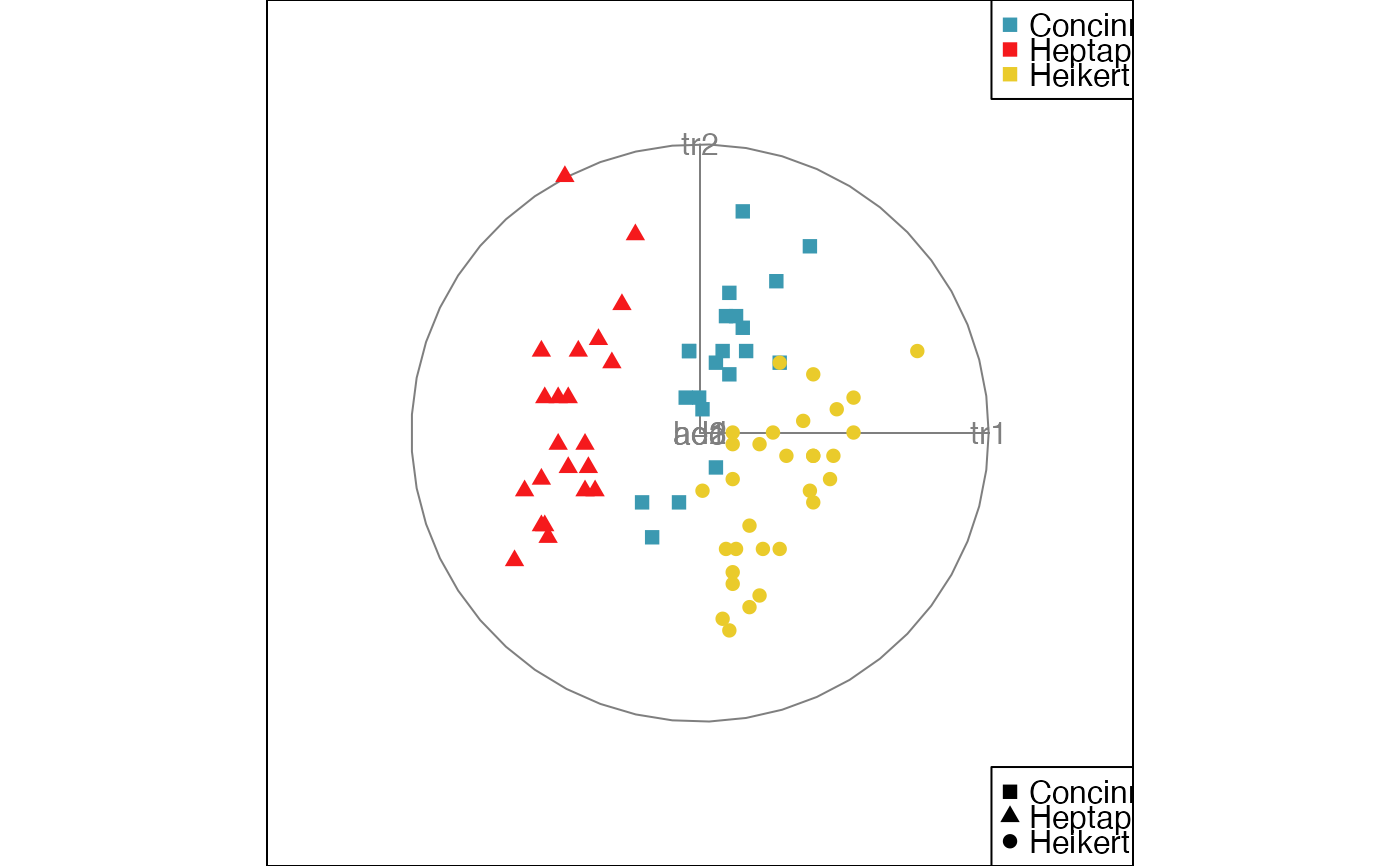
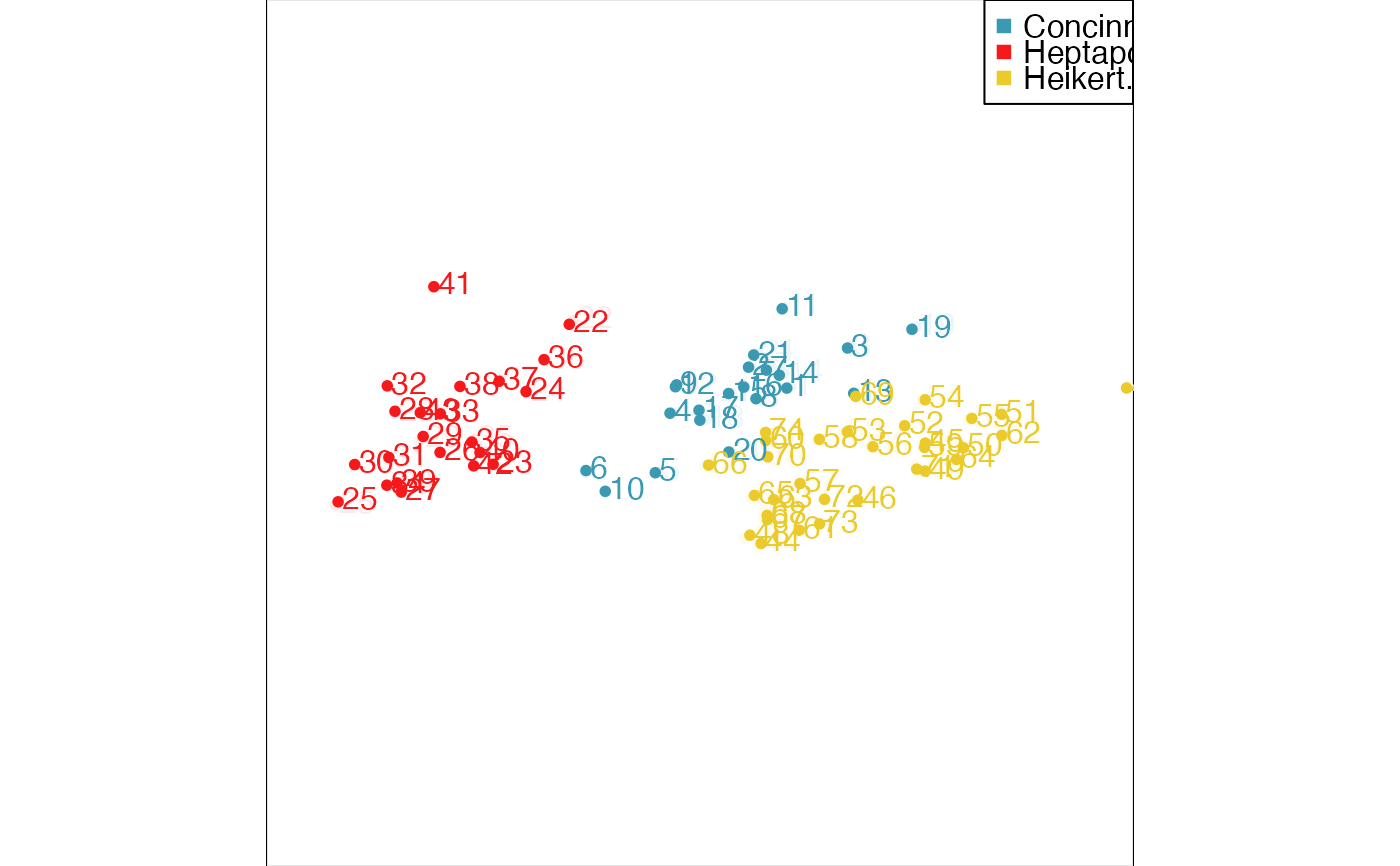
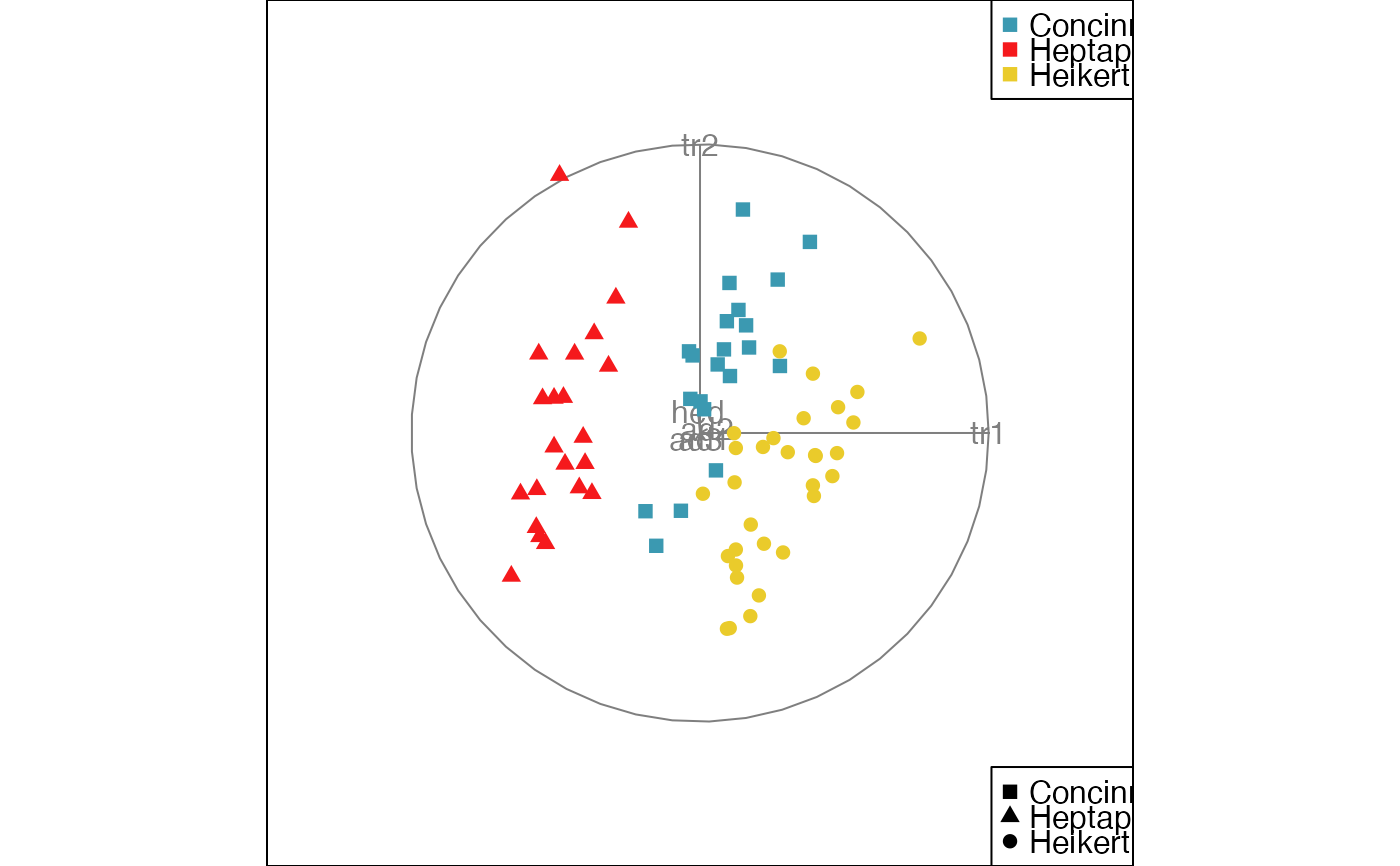 animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species,
obs_labels=as.character(1:nrow(flea)), axes="off")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, -7], col = flea$species,
obs_labels=as.character(1:nrow(flea)), axes="off")
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
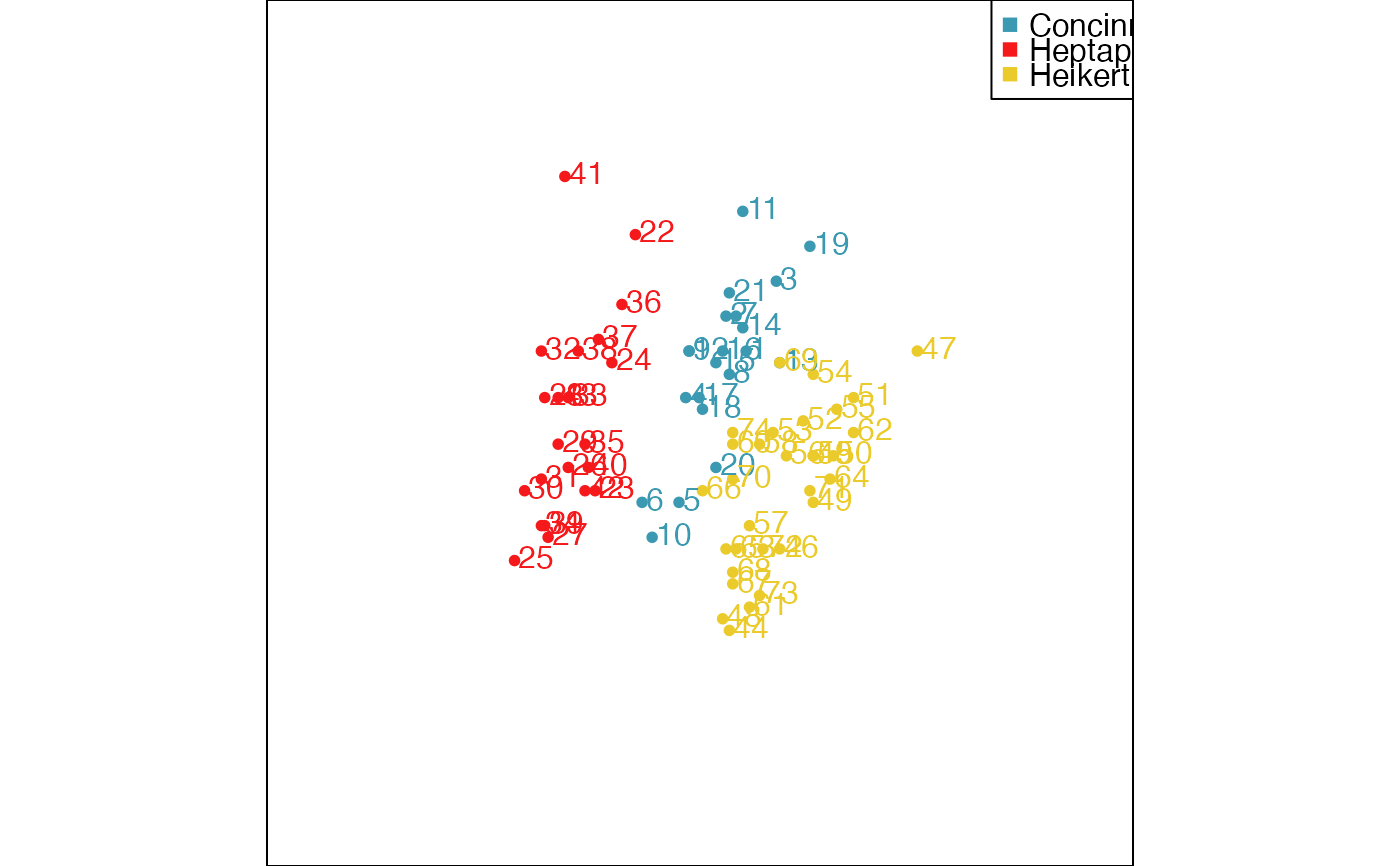
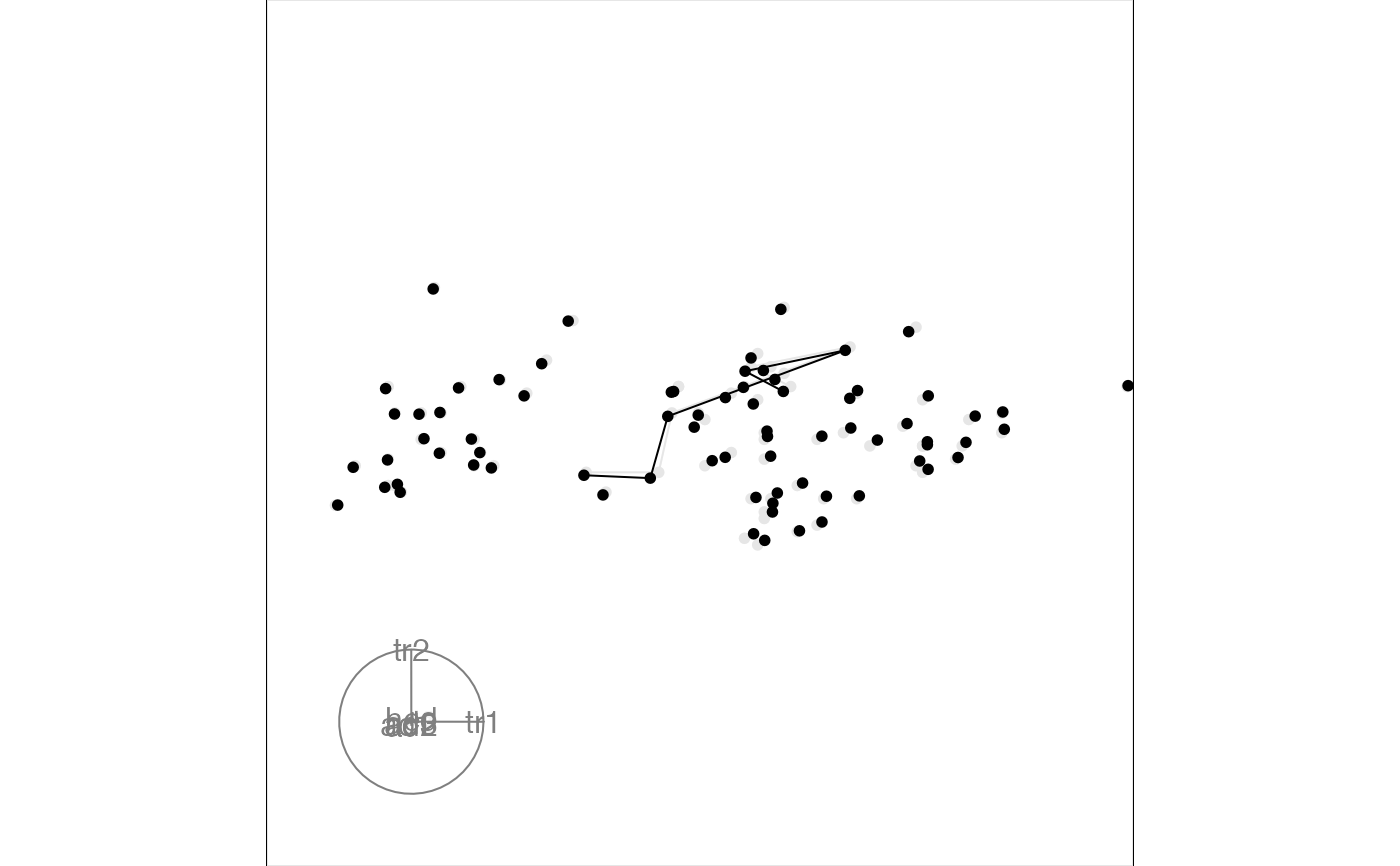
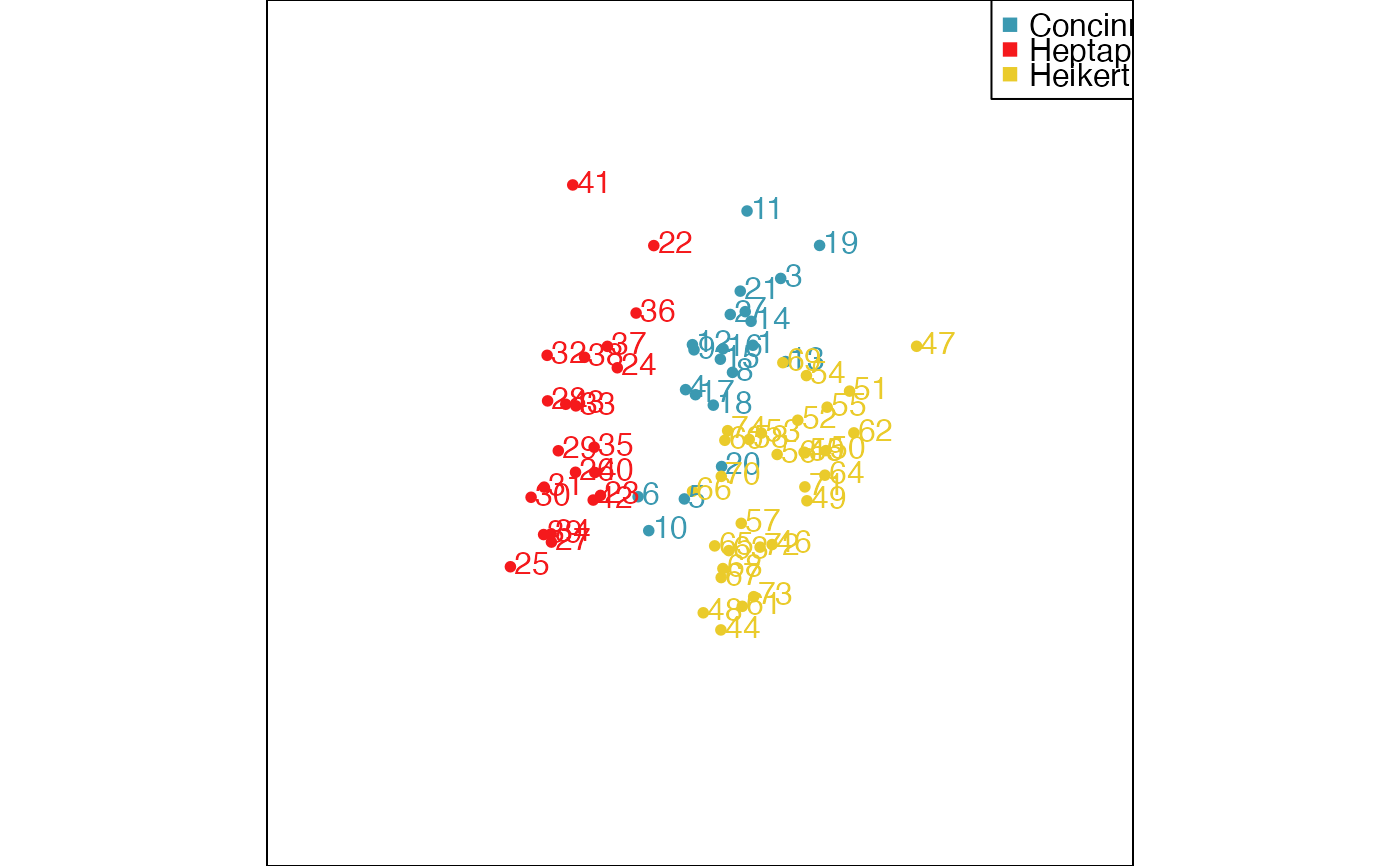 # You can also draw lines
edges <- matrix(c(1:5, 2:6), ncol = 2)
animate(
flea[, 1:6], grand_tour(),
display_xy(axes = "bottomleft", edges = edges)
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
# You can also draw lines
edges <- matrix(c(1:5, 2:6), ncol = 2)
animate(
flea[, 1:6], grand_tour(),
display_xy(axes = "bottomleft", edges = edges)
)
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4

 # An ellipse can be drawn on the data using a specified var-cov
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "off", ellipse=cov(flea[,1:6]))
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
#> Using ellc = 13
# An ellipse can be drawn on the data using a specified var-cov
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6], axes = "off", ellipse=cov(flea[,1:6]))
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
#> Using ellc = 13