This method generates target bases by randomly sampling on the space of all d-dimensional planes in p-space.
grand_tour(d = 2, ...)Details
Usually, you will not call this function directly, but will pass it to
a method that works with tour paths like animate,
save_history or render.
Examples
# All animation methods use the grand tour path by default
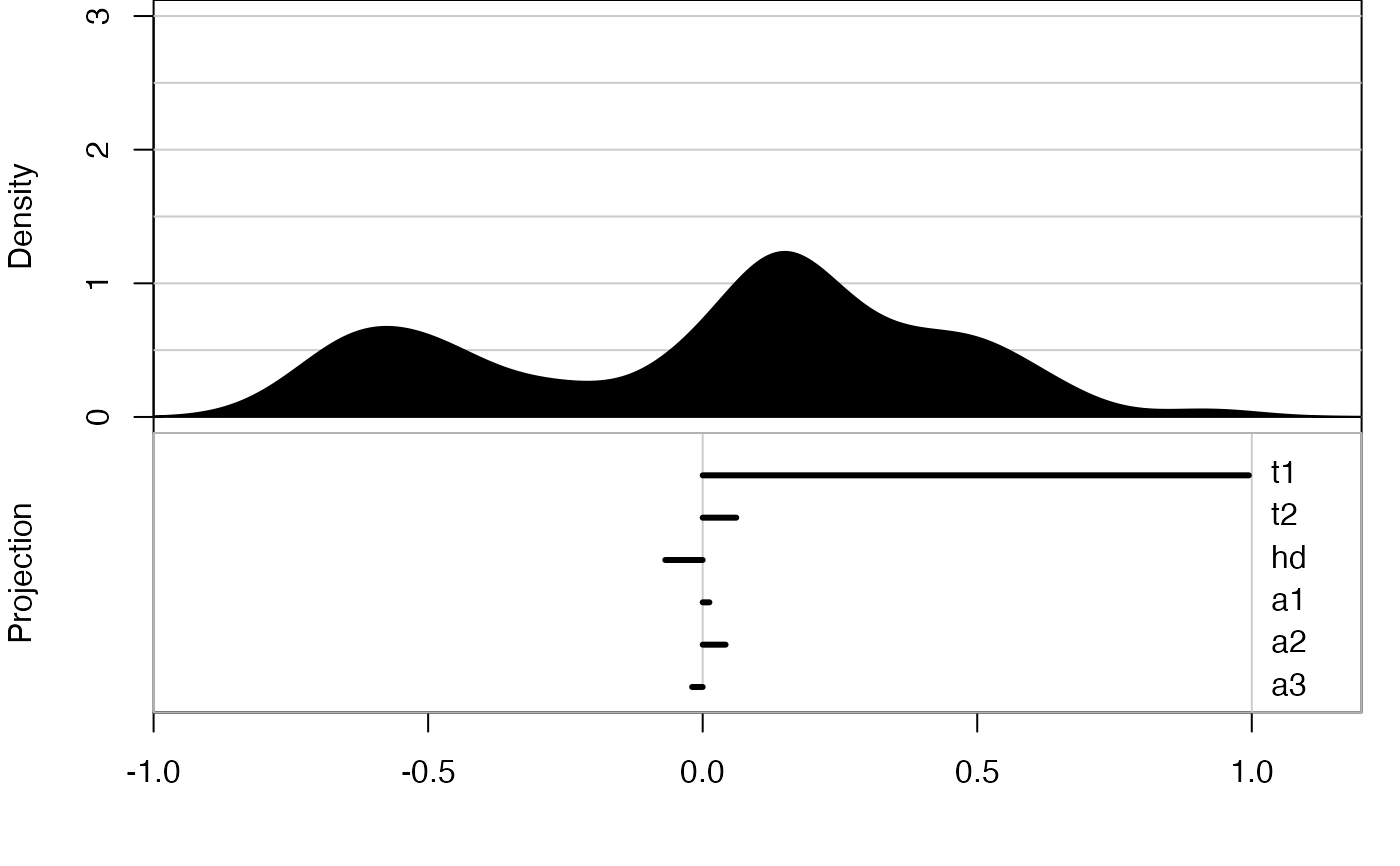
animate_dist(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4

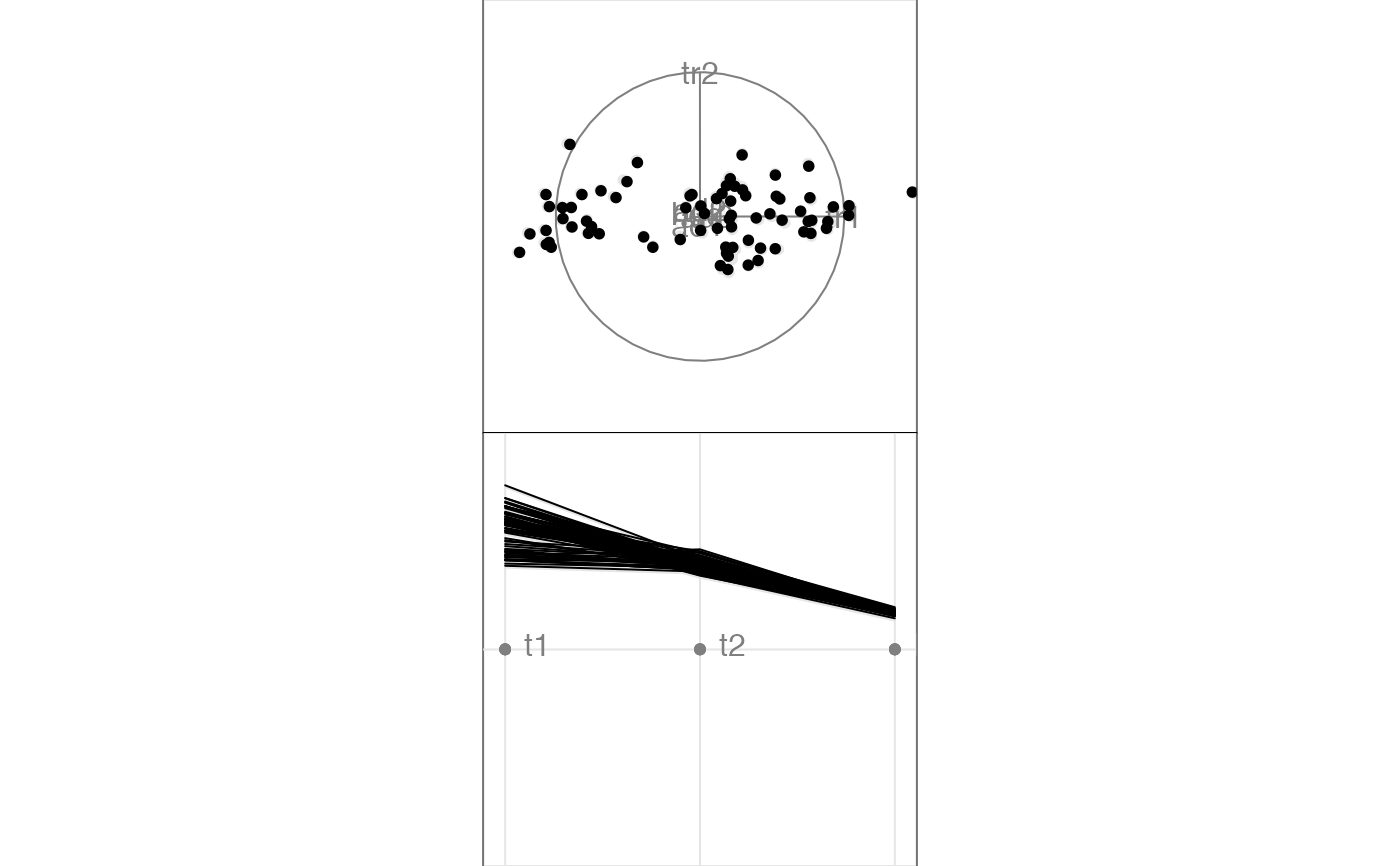
 animate_xy(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
animate_xy(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
#> Using half_range 4.4
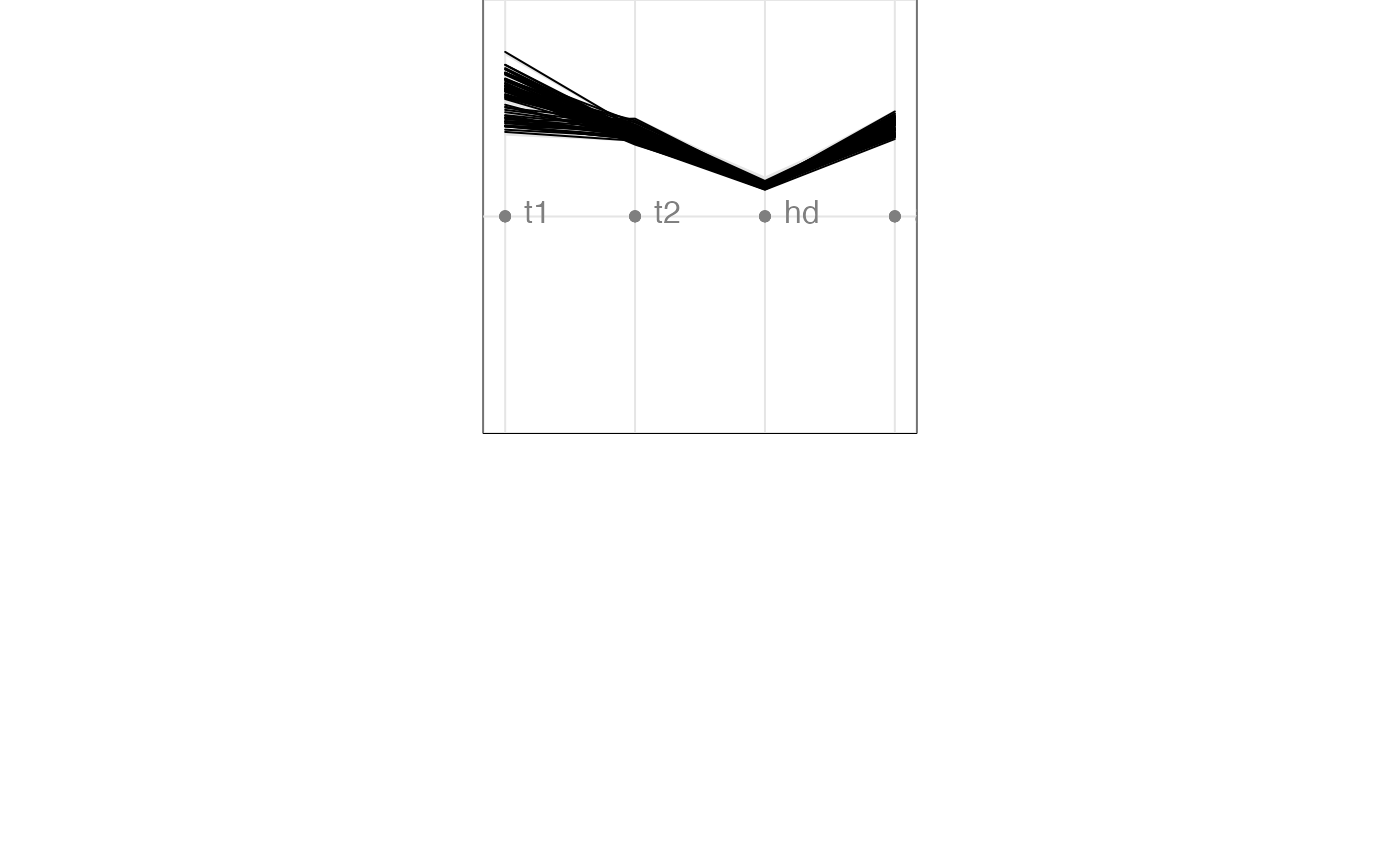
 animate_pcp(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
animate_pcp(flea[, 1:6])
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
 animate_pcp(flea[, 1:6], grand_tour(4))
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
animate_pcp(flea[, 1:6], grand_tour(4))
#> Converting input data to the required matrix format.
 # The grand tour is a function:
tour2d <- grand_tour(2)
is.function(tour2d)
#> [1] TRUE
# with two parameters, the previous projection and the data set
args(tour2d)
#> function (current, data, ...)
#> NULL
# if the previous projection is null, it will generate a starting
# basis, otherwise the argument is ignored
tour2d(NULL, mtcars)
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 1 0
#> [2,] 0 1
#> [3,] 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0
#> [5,] 0 0
#> [6,] 0 0
#> [7,] 0 0
#> [8,] 0 0
#> [9,] 0 0
#> [10,] 0 0
#> [11,] 0 0
# the data argument is just used to determine the correct dimensionality
# of the output matrix
tour2d(NULL, mtcars[, 1:2])
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 1 0
#> [2,] 0 1
# The grand tour is a function:
tour2d <- grand_tour(2)
is.function(tour2d)
#> [1] TRUE
# with two parameters, the previous projection and the data set
args(tour2d)
#> function (current, data, ...)
#> NULL
# if the previous projection is null, it will generate a starting
# basis, otherwise the argument is ignored
tour2d(NULL, mtcars)
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 1 0
#> [2,] 0 1
#> [3,] 0 0
#> [4,] 0 0
#> [5,] 0 0
#> [6,] 0 0
#> [7,] 0 0
#> [8,] 0 0
#> [9,] 0 0
#> [10,] 0 0
#> [11,] 0 0
# the data argument is just used to determine the correct dimensionality
# of the output matrix
tour2d(NULL, mtcars[, 1:2])
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 1 0
#> [2,] 0 1